Nowadays, when we ask people what Data is, they usually refer to their smartphone saying that they generate Data with it. But it could be interesting to put words on this term that is used every day and present everywhere in our environment.
Data is defined by the Oxford dictionary as the quantities, characters, or symbols on which operations are performed by a computer, which may be stored and transmitted in the form of electrical signals and recorded on magnetic, optical, or mechanical recording media. It is also defined as facts and statistics collected together for reference or analysis.
According to this definition, we comprehend that understanding what Data, is a pre-requires for how to use it. Data is everywhere. And a lot of Data is produced in a digital area. Based on a seedscientific article, in 2018, more than 2.5 quintillion bytes of data were created every day. This quantitative explosion of digital data requires new ways of seeing and analyzing the world. This brings us to Big Data.
But, what is Big Data?
The term is pretty self-explanatory. Big Data means mega data, huge data or massive data that is too huge to be analyzed by traditional tools. This data comes from everywhere: Youtube videos, images and videos we post, messages we send, tweets, online shopping transactions records and much more. By definition, Big Data is data that contains greater variety, arriving in increasing volumes, and finally with ever-higher velocity. When we talk about Big Data, the 5V's bubbles to the surface.

What are its benefits?
Big Data is important for companies. Here are some examples:
- A company like Netflix has a huge amount of customers and analyzes the Data of each client around the world to ameliorate the user's experience. As a result, you as a client can just sit and through recommendations, Netflix shows you films that could satisfy you based on multiple parameters. Therefore, the client is satisfied and will always connect to its Netflix account. The analysis of Netflix customers data has helped increase the turnover.
- Certain companies redefined their products based on the collection of information produced by customers and available on social media.
- Banking can detect fraud using the customer's transactions.
We understand that for each company size and in each domain Big Data has a significant role to play.
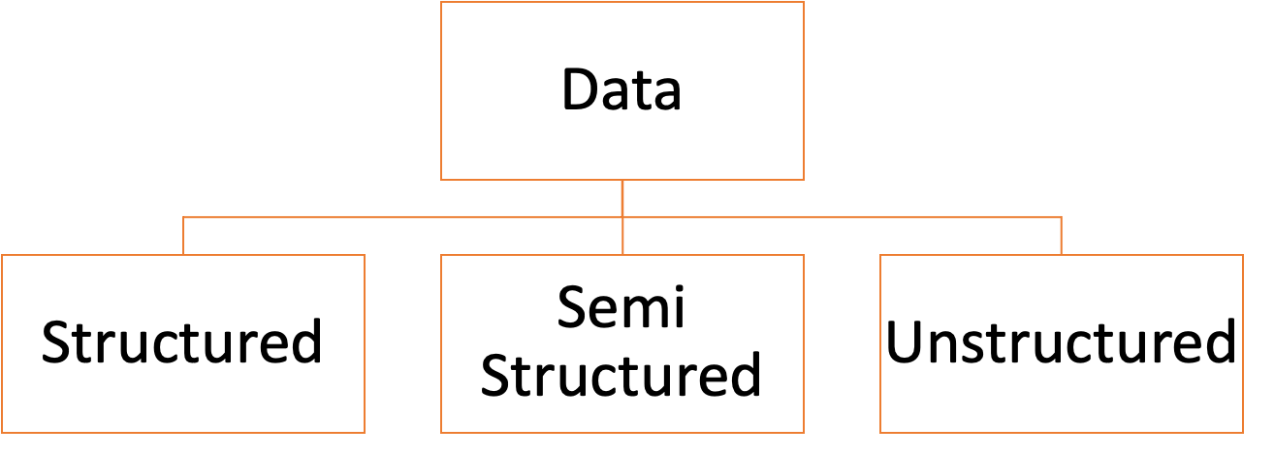
Types of Big Data
Big Data is widely classified into 3 types: structured, unstructured and semi-structured data.
Structured data: It's used to refer to data that is already stored in databases. Data is represented in the form of rows and columns. Also, 20 % of data today is structured.
Here is an example of structured data.
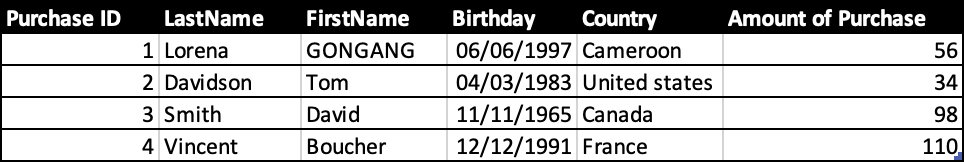 For example, if we do a survey, the information collected would be structured data. Another example of structured data is a Database.
For example, if we do a survey, the information collected would be structured data. Another example of structured data is a Database.
Unstructured data: It has no clear format in storage. This cannot be stored in the form of row columns. It represented 80% of the Data today making extraction a key challenge. Some examples of unstructured data types:
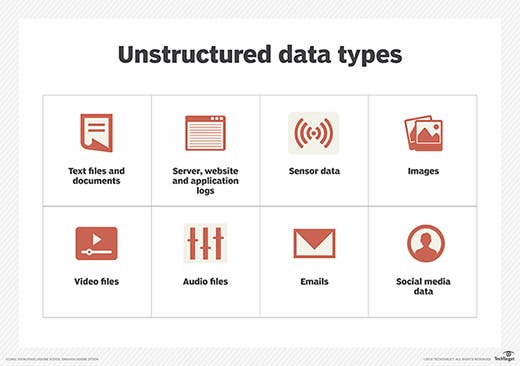 It can be images, files, videos, PDFs, text documents...
It can be images, files, videos, PDFs, text documents...
Semi-structured data: This type of data is difficult to categorize. Sometimes they look structured and sometimes unstructured. Even though it has organizational properties, it can't be stored in a database format. Examples of semi-structured data are XML or JSON documents.
Conclusion
To conclude, we are in an age of Big Data and we contribute as well as anyone else to the generation of data and the exploitation of these by companies.
References
